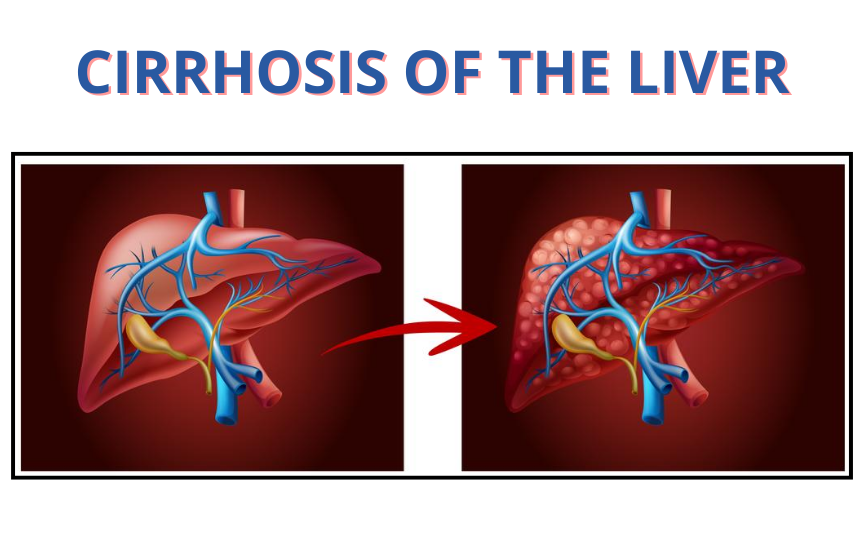
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Cirrhosis is a serious liver disease where the healthy liver tissue gets replaced by scar tissue, making the liver hard and unable to function properly. This happens due to long-term damage caused by different conditions, including alcohol, viral infections, and fatty liver disease. As the liver gets scarred, it struggles to perform important functions like removing toxins, digesting food, and producing essential proteins.
Causes of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis can be caused by multiple factors, including:
- Excessive alcohol consumption – Drinking too much alcohol over time damages liver cells.
- Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C – Long-term viral infections can lead to liver damage.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – Common in overweight and diabetic individuals, leading to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis – The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells.
- Wilson’s Disease – A rare genetic condition where copper builds up in the liver.
- Hemochromatosis – A disorder where excess iron deposits damage the liver.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
In the early stages, cirrhosis may not cause any symptoms and is often detected accidentally during routine health check-ups. As the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
✔ Weakness and tiredness
✔ Loss of appetite and weight loss
✔ Swelling in the feet (pedal edema) and fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites)
✔ Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
✔ Vomiting of blood or black stools (due to internal bleeding)
✔ Confusion, memory loss, or unconsciousness (hepatic encephalopathy)
✔ Low urine output due to kidney issues
Stages of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis progresses in two stages:
🔹 Compensated Cirrhosis – The liver is damaged but still functions well, and there may be no noticeable symptoms.
🔹 Decompensated Cirrhosis – The liver starts failing, and serious complications like internal bleeding, confusion, and severe swelling occur.
Complications of Cirrhosis
If untreated, cirrhosis can lead to life-threatening complications, including:
🩸 Variceal Bleeding – Enlarged veins in the food pipe may burst and cause severe bleeding.
💧 Ascites & Edema – Fluid buildup in the abdomen and legs.
🧠 Hepatic Encephalopathy – Toxin buildup in the brain causing confusion and drowsiness.
❤️ Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma) – Cirrhosis increases the risk of liver cancer.
🫀 Kidney & Lung Failure – Severe liver damage affects the kidneys and lungs.
Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
Doctors use different tests to confirm cirrhosis:
✔ Liver Function Tests (LFTs) – Checks liver enzymes and bilirubin levels.
✔ Ultrasound, Fibro-scan, CT Scan, or MRI – Helps assess liver stiffness and scarring.
✔ Liver Biopsy – A small tissue sample is taken to check liver damage.
Treatment for Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis cannot be reversed, but early treatment can slow its progression. The goal is to control symptoms, manage complications, and prevent further liver damage.
🟢 Lifestyle Changes
✅ Stop alcohol completely to prevent further damage.
✅ Maintain a healthy weight and eat a high-protein, balanced diet.
✅ Regular exercise and avoiding junk food.
🟢 Medications
✔ Antivirals for Hepatitis B & C to slow liver damage.
✔ Steroids for Autoimmune Hepatitis.
✔ Diuretics (water pills) to reduce swelling.
✔ Beta-blockers to prevent variceal bleeding.
✔ Lactulose and L-Ornithine L-Aspartate for confusion due to toxin buildup.
🟢 Liver Transplant
In advanced cirrhosis, when the liver completely fails, a liver transplant may be the only life-saving option.
Can Cirrhosis be Prevented?
✅ Get vaccinated for Hepatitis B.
✅ Limit alcohol and avoid smoking.
✅ Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly.
✅ Go for regular health check-ups, especially if you have diabetes or fatty liver.
Cirrhosis is a serious but manageable condition. Early diagnosis and the right treatment can help improve quality of life and prevent severe complications. If you or a loved one have symptoms of liver disease, consult a gastroenterologist immediately.